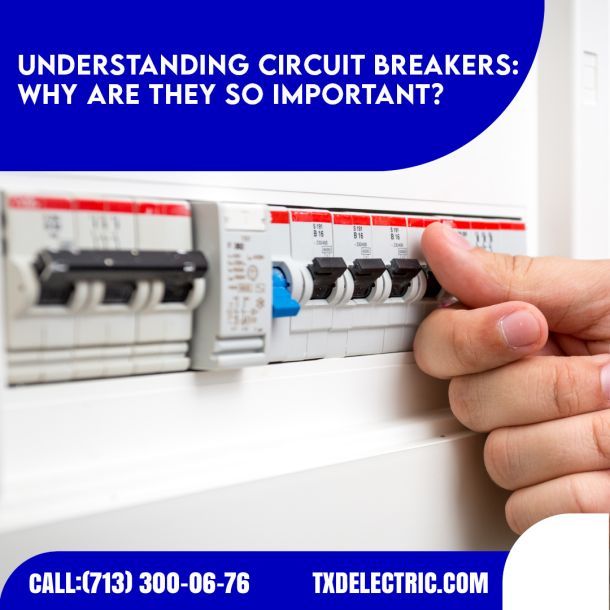
The Essential Role of Transformers in Electrical Power Distribution
When it comes to the distribution of electrical power, transformers are unsung heroes that quietly enable electricity to travel from power plants to our homes and businesses. These essential devices play a crucial role in adjusting voltage levels to make long-distance transmission and local distribution possible. In this blog, we'll explore the importance of transformers in the world of electrical power distribution.
What Are Transformers?
Transformers are electrical devices designed to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. They consist of two coils of wire, known as primary and secondary windings, wrapped around a magnetic core. Transformers can either increase (step up) or decrease (step down) voltage levels, depending on their application.
Voltage Transformation
- Long-Distance Transmission
Power plants generate electricity at high voltages for efficient long-distance transmission. High-voltage electricity travels more efficiently through power lines, reducing energy loss during transport. Transformers at substations step up the voltage for transmission.
- Local Distribution
High-voltage electricity is not suitable for household and business use, as it poses a safety risk and could damage appliances. Transformers located in neighborhoods and commercial areas step down the voltage to safer levels for distribution.
Loss Reduction
- Minimizing Energy Loss
Energy loss occurs when electricity travels over long distances. Transformers help mitigate these losses by increasing voltage at the source, and then stepping it down at the destination. This results in more efficient energy transfer and lower power wastage.
Safety and Reliability
- Isolation and Grounding
Transformers provide electrical isolation between primary and secondary windings, which enhances safety by preventing direct electrical contact between high-voltage power lines and low-voltage distribution lines. They also allow for grounding to protect against electrical faults.
Types of Transformers
- Distribution Transformers
These transformers are commonly found in neighborhoods and commercial areas, stepping down high-voltage power to levels suitable for homes and businesses.
- Power Transformers
Power transformers are used in substations and power plants to step up or step down voltage levels as needed for long-distance transmission and local distribution.
- Specialty Transformers
Specialty transformers, like instrument transformers, serve unique purposes, such as measuring voltage and current for control and protective devices.
Maintenance and Efficiency
Proper maintenance of transformers is vital for ensuring their efficiency and longevity. Regular inspections and preventive measures help detect issues and prevent failures. These include oil sampling, insulation resistance testing, and temperature monitoring.
Transformers are at the heart of electrical power distribution, enabling electricity to be generated at power plants and safely delivered to our homes and businesses. Without transformers, the efficient transmission and safe distribution of electrical power would be nearly impossible.
Understanding the essential role of transformers in the power distribution process highlights their significance in maintaining the reliability and efficiency of our electrical infrastructure. As technology advances, transformers continue to evolve, becoming more efficient and environmentally friendly, making them even more vital in the ever-changing landscape of electrical power distribution.
Source: name
As licensed contractors, we provide our clients with a comprehensive approach to all of their projects, specializing in a a wide range of services. Since we founded our business in 2000, we’ve been committed to our clients’ needs and satisfaction.
Do you have a project or idea in mind that you want to get started on? We are here to make it happen. Get in touch to learn what we can do for you today.

 Attic Fans
Attic Fans Patio Lighting
Patio Lighting